Difference between revisions of "Malate-anaplerotic pathway control state"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{MitoPedia | {{MitoPedia | ||
|abbr=M | |abbr=M | ||
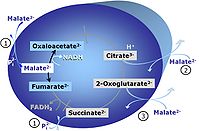
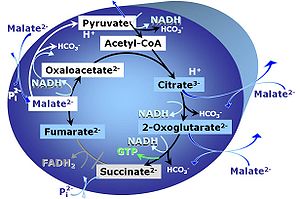
|description=[[File:M.jpg|left|200px|M]] '''M''': [[Malate]] alone does not support respiration of mt-preparations if [[oxaloacetate]] cannot be metabolized further in the absence of a source of acetyl-CoA. Transport of oxaloacetate across the inner mt-membrane is restricted particularly in liver. Mitochondrial citrate and 2-oxoglutarate (α-ketoglutarate) are depleted by antiport with malate. [[Succinate]] is lost from the mitochondria through the dicarboxylate carrier. OXPHOS capacity with malate alone is only 1.3% of that with [[PM |Pyruvate&Malate]] in isolated rat skeletal muscle mitochondria. Many mammalian and non-mammalian mitochondria have a mt-isoform of NADP<sup>+-</sup> or NAD(P)<big>+</big>-dependent [[malic enzyme]] (mtME), the latter being particularly active in proliferating cells. Then the [[anaplerotic pathway control state]] with malate alone supports high respiratory activities. | |description=[[File:M.jpg|left|200px|M]] '''M''': [[Malate]] alone does not support respiration of mt-preparations if [[oxaloacetate]] cannot be metabolized further in the absence of a source of acetyl-CoA. Transport of oxaloacetate across the inner mt-membrane is restricted particularly in liver. Mitochondrial citrate and 2-oxoglutarate (α-ketoglutarate) are depleted by antiport with malate. [[Succinate]] is lost from the mitochondria through the dicarboxylate carrier. OXPHOS capacity with malate alone is only 1.3% of that with [[PM |Pyruvate&Malate]] in isolated rat skeletal muscle mitochondria. Many mammalian and non-mammalian mitochondria have a mt-isoform of NADP<sup>+-</sup> or NAD(P)<big>+</big>-dependent [[malic enzyme]] (mtME), the latter being particularly active in proliferating cells. Then the [[anaplerotic pathway control state]] with malate alone (aN) supports high respiratory activities comparable to the NADH-linked pathway control states (N) with with pyruvate&malate or glutamate&malate substrate combinations ([[PM pathway control state]], [[GM pathway control state]]). | ||
|info=[[Gnaiger 2014 MitoPathways]] - Chapter 3.1 | |info=[[Gnaiger 2014 MitoPathways]] - Chapter 3.1 | ||
}} | }} | ||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
|mitopedia concept=SUIT state | |mitopedia concept=SUIT state | ||
}} | }} | ||
Communicated by [[Gnaiger E]] 2016-01-24, edited 2016-11-30. | |||
[[File:M-malic enzyme.jpg|right|300px|M and malic enzyme]] | [[File:M-malic enzyme.jpg|right|300px|M and malic enzyme]] | ||
Revision as of 10:01, 30 November 2016
- high-resolution terminology - matching measurements at high-resolution
Malate-anaplerotic pathway control state
Description
M: Malate alone does not support respiration of mt-preparations if oxaloacetate cannot be metabolized further in the absence of a source of acetyl-CoA. Transport of oxaloacetate across the inner mt-membrane is restricted particularly in liver. Mitochondrial citrate and 2-oxoglutarate (α-ketoglutarate) are depleted by antiport with malate. Succinate is lost from the mitochondria through the dicarboxylate carrier. OXPHOS capacity with malate alone is only 1.3% of that with Pyruvate&Malate in isolated rat skeletal muscle mitochondria. Many mammalian and non-mammalian mitochondria have a mt-isoform of NADP+- or NAD(P)+-dependent malic enzyme (mtME), the latter being particularly active in proliferating cells. Then the anaplerotic pathway control state with malate alone (aN) supports high respiratory activities comparable to the NADH-linked pathway control states (N) with with pyruvate&malate or glutamate&malate substrate combinations (PM pathway control state, GM pathway control state).
Abbreviation: M
Reference: Gnaiger 2014 MitoPathways - Chapter 3.1
MitoPedia concepts:
SUIT state
Communicated by Gnaiger E 2016-01-24, edited 2016-11-30.