Difference between revisions of "Motive unit"
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
For the [[protonmotive force]] the motive entity is the proton with charge number ''z''=1. The protonmotive force is expressed in the electrical or molar format with MU J/C=V or J/mol=Jol, respectively. The conjugated flows, ''I'', are expressed in corresponding electrical or molar formats, C/s = A or mol/s, respectively. | For the [[protonmotive force]] the motive entity is the proton with charge number ''z''=1. The protonmotive force is expressed in the electrical or molar format with MU J/C=V or J/mol=Jol, respectively. The conjugated flows, ''I'', are expressed in corresponding electrical or molar formats, C/s = A or mol/s, respectively. | ||
The charge number, ''z'', is not involved in the conversion of motive units (see Table below), in contrast to a change not only of units but transition from the entity (e.g., O<sub>2</sub> with ''z''=4) to the entity of charge. The ratio of electrons per O<sub>2</sub> (''z''<sub>O2</sub>=4) is multiplied by the elementary charge (''e'', coulombs per electron), which yields coulombs per O<sub>2</sub> [C∙x-1]. This is multiplied with ''N''<sub>A</sub> (O<sub>2</sub> molecules per mole O<sub>2</sub> [x∙mol<sup>-1</sup>]), thus obtaining for ''ze''∙''N''<sub>A</sub> the ratio of coulombs charge per mole O<sub>2</sub> [C∙mol<sup>-1</sup>]. | The charge number, ''z'', is not involved in the conversion of motive units (see Table below), in contrast to a change not only of units but transition from the entity (e.g., O<sub>2</sub> with ''z''=4) to the entity of charge. The ratio of electrons per O<sub>2</sub> (''z''<sub>O2</sub>=4) is multiplied by the elementary charge (''e'', coulombs per electron), which yields coulombs per O<sub>2</sub> [C∙x<sup>-1</sup>]. This is multiplied with ''N''<sub>A</sub> (O<sub>2</sub> molecules per mole O<sub>2</sub> [x∙mol<sup>-1</sup>]), thus obtaining for ''ze''∙''N''<sub>A</sub> the ratio of coulombs charge per mole O<sub>2</sub> [C∙mol<sup>-1</sup>]. | ||
}} | }} | ||
Communicated by [[Gnaiger E]] 2018-10-14 | Communicated by [[Gnaiger E]] 2018-10-14 | ||
Revision as of 19:42, 14 October 2018
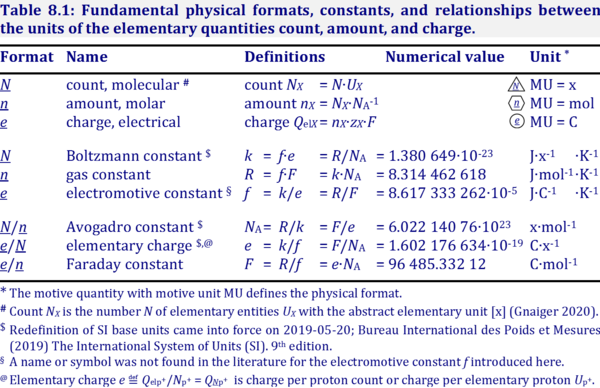
Description
The motive unit [MU] is the SI unit in which the motive entity (transformant) of a transformation is expressed, which depends on the energy transformation under study and on the chosen format. Fundamental MU for electrochemical transformation are:
- Molecular or particle format, N; MU = x
- Molar format, n; MU = mol
- Electrical format, e; MU = C
For the protonmotive force the motive entity is the proton with charge number z=1. The protonmotive force is expressed in the electrical or molar format with MU J/C=V or J/mol=Jol, respectively. The conjugated flows, I, are expressed in corresponding electrical or molar formats, C/s = A or mol/s, respectively.
The charge number, z, is not involved in the conversion of motive units (see Table below), in contrast to a change not only of units but transition from the entity (e.g., O2 with z=4) to the entity of charge. The ratio of electrons per O2 (zO2=4) is multiplied by the elementary charge (e, coulombs per electron), which yields coulombs per O2 [C∙x-1]. This is multiplied with NA (O2 molecules per mole O2 [x∙mol-1]), thus obtaining for ze∙NA the ratio of coulombs charge per mole O2 [C∙mol-1].
Abbreviation: MU
Communicated by Gnaiger E 2018-10-14
MitoPedia concepts: Ergodynamics