Difference between revisions of "Motive unit"
(Created page with "{{MitoPedia |abbr=MU |description=The '''motive unit''' [MU] is the SI unit in which the motive entity (transformant) of a transformation is expressed, which depends on th...") |
|||
| (9 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{MitoPedia | {{MitoPedia | ||
|abbr=MU | |abbr=MU | ||
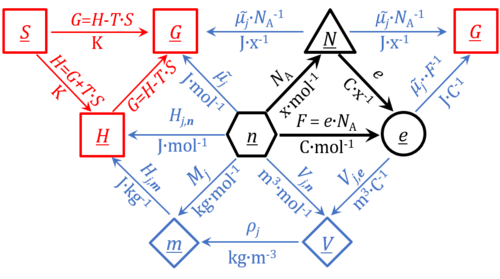
|description=The '''motive unit''' [MU] is the SI unit in which the [[motive entity]] (transformant) of a transformation is expressed, which depends on the energy transformation under study and on the chosen format. Fundamental MU for electrochemical | |description=The '''motive unit''' [MU] is the variable SI unit in which the [[motive entity]] (transformant) of a transformation is expressed, which depends on the energy transformation under study and on the chosen [[format]]. Fundamental MU for electrochemical transformations are: | ||
* | * MU = x, for the particle or molecular format, <u>''N''</u> | ||
* MU = mol, for the chemical or molar format, <u>''n''</u> | |||
* MU = C, for the electrical format, <u>''e''</u>; | |||
For the [[protonmotive force]] the motive entity is the proton with charge number ''z''=1. The protonmotive force is expressed in the electrical or molar format with MU J/C=V or J/mol=Jol, respectively. The conjugated flows, ''I'', are expressed in corresponding electrical or molar formats, C/s = A or mol/s, respectively. | |||
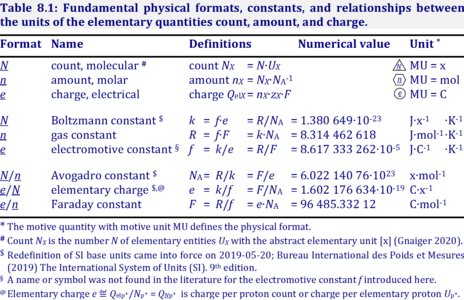
The [[charge number]], ''z'', has to be considered in the conversion of motive units (compare Table below), if a change not only of units but a transition between the entity [[elementary charge]] and an entity with charge number different from unity is involved (''e.g.'', O<sub>2</sub> with ''z''=4). The ratio of elementary charges per O<sub>2</sub> molecule (''z''<sub>O<small>2</small></sub>=4) is multiplied by the elementary charge (''e'', coulombs per electron), which yields coulombs per O<sub>2</sub> [C∙x<sup>-1</sup>]. This in turn is multiplied with the [[Avogadro constant]], ''N''<sub>A</sub> (O<sub>2</sub> molecules per mole O<sub>2</sub> [x∙mol<sup>-1</sup>]), thus obtaining for ''ze''∙''N''<sub>A</sub> the ratio of elementary charges [C] per amount of O<sub>2</sub> [mol<sup>-1</sup>]. The conversion factor for O<sub>2</sub> is 385.94132 C∙mmol<sup>-1</sup>. | |||
}} | }} | ||
Communicated by [[Gnaiger E]] 2018-10-20 | |||
<gallery mode=default perrow=2 widths="500px" heights="300px"> | |||
File:Table Physical constants.png | |||
File:Motive formats and units.png|Converstion between different motive formats and corresponding motive units | |||
</gallery> | |||
{{Template:Keywords: Normalization}} | |||
{{Keywords: SI base units}} | |||
{{MitoPedia concepts | {{MitoPedia concepts | ||
|mitopedia concept=Ergodynamics | |mitopedia concept=Ergodynamics | ||
}} | }} | ||
Revision as of 06:27, 18 May 2020
Description
The motive unit [MU] is the variable SI unit in which the motive entity (transformant) of a transformation is expressed, which depends on the energy transformation under study and on the chosen format. Fundamental MU for electrochemical transformations are:
- MU = x, for the particle or molecular format, N
- MU = mol, for the chemical or molar format, n
- MU = C, for the electrical format, e;
For the protonmotive force the motive entity is the proton with charge number z=1. The protonmotive force is expressed in the electrical or molar format with MU J/C=V or J/mol=Jol, respectively. The conjugated flows, I, are expressed in corresponding electrical or molar formats, C/s = A or mol/s, respectively.
The charge number, z, has to be considered in the conversion of motive units (compare Table below), if a change not only of units but a transition between the entity elementary charge and an entity with charge number different from unity is involved (e.g., O2 with z=4). The ratio of elementary charges per O2 molecule (zO2=4) is multiplied by the elementary charge (e, coulombs per electron), which yields coulombs per O2 [C∙x-1]. This in turn is multiplied with the Avogadro constant, NA (O2 molecules per mole O2 [x∙mol-1]), thus obtaining for ze∙NA the ratio of elementary charges [C] per amount of O2 [mol-1]. The conversion factor for O2 is 385.94132 C∙mmol-1.
Abbreviation: MU
Communicated by Gnaiger E 2018-10-20
- Bioblast links: Normalization - >>>>>>> - Click on [Expand] or [Collapse] - >>>>>>>
- Quantities for normalization
- » Count in contrast to Number
- » Mitochondrial marker
- » O2k-Protocols: mitochondrial and marker-enzymes
- » Citrate synthase activity
- Quantities for normalization
- General
- Related keyword lists
- Bioblast links: SI base units - >>>>>>> - Click on [Expand] or [Collapse] - >>>>>>>
- Entity, count, and number, and SI base quantities / SI base units
Quantity name Symbol Unit name Symbol Comment elementary UX elementary unit [x] UX, UB; [x] not in SI count NX elementary unit [x] NX, NB; [x] not in SI number N - dimensionless = NX·UX-1 amount of substance nB mole [mol] nX, nB electric current I ampere [A] A = C·s-1 time t second [s] length l meter [m] SI: metre mass m kilogram [kg] thermodynamic temperature T kelvin [K] luminous intensity IV candela [cd]
- Fundamental relationships
- » Avogadro constant NA
- » Boltzmann constant k
- » elementary charge e
- » Faraday constant F
- » gas constant R
- » electrochemical constant f
- Fundamental relationships
- SI and related concepts
MitoPedia concepts:
Ergodynamics