Difference between revisions of "Steady state"
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
<gallery mode=default perrow=2 widths="600px" heights="400px"> | <gallery mode=default perrow=2 widths="600px" heights="400px"> | ||
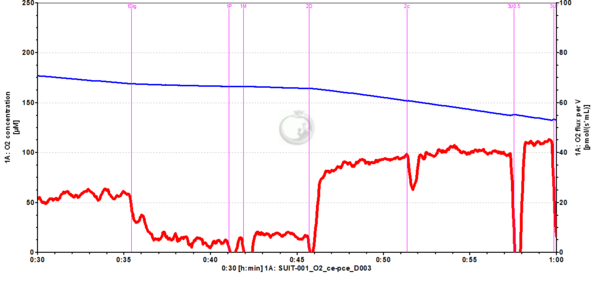
File:ADP_no_steady_state_O2flux_01.png | '''Figure 1'''. Oxygen flux per volume (right axis, red trace) is not stable in the [[OXPHOS capacity| OXPHOS state]] (2D). Consequently, OXPHOS capacity is underestimated. The addition of cytochrome ''c'' (2c), if stability has not yet been reached in the OXPHOS state, leads to an overestimation of the [[Cytochrome c control factor|cytochrome ''c'' effect]], since the increase in the oxygen flux is not due to the cytochrome ''c'' addition, but instead because flux increases further over time (see Figure 2 for more detail). | File:ADP_no_steady_state_O2flux_01.png | '''Figure 1'''. Oxygen flux per volume (right axis, red trace) is not stable in the [[OXPHOS capacity| OXPHOS state]] (2D). Consequently, OXPHOS capacity is underestimated. The addition of cytochrome ''c'' (2c), if stability has not yet been reached in the OXPHOS state, leads to an overestimation of the [[Cytochrome c control factor|cytochrome ''c'' effect]], since the increase in the oxygen flux is not due to the cytochrome ''c'' addition, but instead because flux increases further over time (see Figure 2 for more detail). Cryopreserved HEK-293 cells. Experiment 2020-01-22 P1-03. | ||
File:ADP_no_steady_state_O2flux_02.png | '''Figure 2'''. Illustration of (''1'') the underestimation of OXPHOS capacity (2D), and (2) the overestimation of the [[Cytochrome c control factor|cytochrome ''c'' effect]]. The increase of oxygen flux is indicated by the straight line (from 2D to 2c) is not due to the cytochrome ''c'' addition. More time would have been requred to reach a stable flux before step 2c. | File:ADP_no_steady_state_O2flux_02.png | '''Figure 2'''. Illustration of (''1'') the underestimation of OXPHOS capacity (2D), and (2) the overestimation of the [[Cytochrome c control factor|cytochrome ''c'' effect]]. The increase of oxygen flux is indicated by the straight line (from 2D to 2c) is not due to the cytochrome ''c'' addition. More time would have been requred to reach a stable flux before step 2c. Cryopreserved HEK-293 cells. Experiment 2020-01-22 P1-03. | ||
File:ADP_steady_state_O2flux_01.png | '''Figure 3'''. Oxygen flux is stable in 2D, therefore a proper result on [[OXPHOS capacity]] is obtained. In this case, the addition of cytochrome ''c'' (2c) does not lead to an overestimation of the [[cytochrome c control factor]]. | File:ADP_steady_state_O2flux_01.png | '''Figure 3'''. Oxygen flux is stable in 2D, therefore a proper result on [[OXPHOS capacity]] is obtained. In this case, the addition of cytochrome ''c'' (2c) does not lead to an overestimation of the [[cytochrome c control factor]]. Cryopreserved HEK-293 cells. Experiment 2020-01-22 P5-03_D003 and D007 tests. | ||
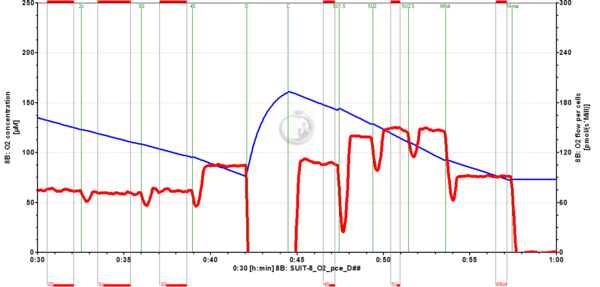
File:ADP_steady_state_O2flux_02.png | '''Figure 4'''. Oxygen flux may need time to stabilize (see 2D). Stabilization time is a property of the mitochondrial sample and varies in different pathophysiological states. Stability of flux can be evaluated with the O2k and DatLab at high-resolution by real-time display of oxygen flux (red line). Oxygen concentration (blue line) may appear to show a sufficiently stable slope, while the actual (negative) slope shown by the red line yields the required sensitivity for evaluation of flux in a respiratory 'steady state'. It is important to wait until a steady state is reached to avoid underestimation of respiratory fluxes. Oxygen concentrations may decline below a lower limit in the closed system, in which case a reoxygenation must be performed by intermittently opening the chamber. An instrumental stabilization time must be taken into account after closing the chamber, to avoid an artefact of overestimation of respiratory flux. Therefore, after a reoxygenation it is equally important to wait until an instrumental steady state is reached for measurement of flux. | File:ADP_steady_state_O2flux_02.png | '''Figure 4'''. Oxygen flux may need time to stabilize (see 2D). Stabilization time is a property of the mitochondrial sample and varies in different pathophysiological states. Stability of flux can be evaluated with the O2k and DatLab at high-resolution by real-time display of oxygen flux (red line). Oxygen concentration (blue line) may appear to show a sufficiently stable slope, while the actual (negative) slope shown by the red line yields the required sensitivity for evaluation of flux in a respiratory 'steady state'. It is important to wait until a steady state is reached to avoid underestimation of respiratory fluxes. Oxygen concentrations may decline below a lower limit in the closed system, in which case a reoxygenation must be performed by intermittently opening the chamber. An instrumental stabilization time must be taken into account after closing the chamber, to avoid an artefact of overestimation of respiratory flux. Therefore, after a reoxygenation it is equally important to wait until an instrumental steady state is reached for measurement of flux. Cryopreserved HEK-293 cells. Experiment 2018-12-18 P8-02. | ||
|- | |- | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
<gallery mode=default perrow=2 widths="600px" heights="400px"> | <gallery mode=default perrow=2 widths="600px" heights="400px"> | ||
File:Rot_steady_state_O2flux_02.png | '''Figure 5'''. [[Rotenone]] (Complex I inhibitor) addition in the presence of [[NS-pathway control state|NS-linked substrates]] (PGMS) and uncoupler in [[ET-capacity|ET-state]] (NS<sub>''E''</sub>) allows for measurement of [[Succinate-pathway|S-pathway]] capacity in the ET state (S<sub>''E''</sub>, 6Rot). In many cases, inhibition of flux by rotenone is very fast as shown by a quick transition to a stable flux in the inhibited respiratory state. | File:Rot_steady_state_O2flux_02.png | '''Figure 5'''. [[Rotenone]] (Complex I inhibitor) addition in the presence of [[NS-pathway control state|NS-linked substrates]] (PGMS) and uncoupler in [[ET-capacity|ET-state]] (NS<sub>''E''</sub>) allows for measurement of [[Succinate-pathway|S-pathway]] capacity in the ET state (S<sub>''E''</sub>, 6Rot). In many cases, inhibition of flux by rotenone is very fast as shown by a quick transition to a stable flux in the inhibited respiratory state. HEK-293 cells. Experiment 2018-10-23 P8-02. | ||
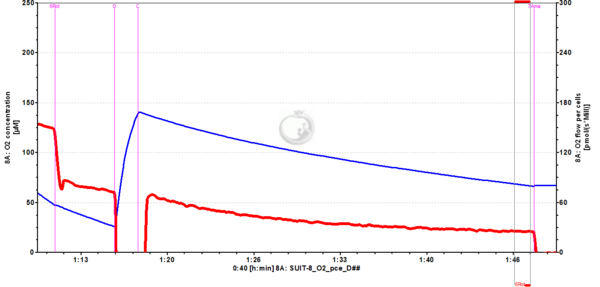
File:Rot_steady_state_O2flux_01.png | '''Figure 6'''. Inhibition by rotenone (or other inhibitors, ''e.g.'' [[Antimycin A]]) may require a long time until a new steady respiratory state is reached. This is observed particulary in permeabilized muscle fibers, but may apply to other [[MitoPedia: Sample preparations|mitochondrial preparations]]). It is important to wait until a stable flux is reached to avoid overestimation of respiratory fluxes. | File:Rot_steady_state_O2flux_01.png | '''Figure 6'''. Inhibition by rotenone (or other inhibitors, ''e.g.'' [[Antimycin A]]) may require a long time until a new steady respiratory state is reached. This is observed particulary in permeabilized muscle fibers, but may apply to other [[MitoPedia: Sample preparations|mitochondrial preparations]]). It is important to wait until a stable flux is reached to avoid overestimation of respiratory fluxes. HEK-293 cells. Experiment 2018-10-23 P8-02. | ||
|- | |- | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Revision as of 09:13, 3 June 2020
Description
A system is in a steady state if the state variables of a dynamic system do not change over time due to exchange processes with the environment, which compensate for internal dissipative transformations — such as chemical reactions or diffusion — and thus prevent any changes of the system and externalize dissipative changes to the environment. The dynamic nature of the steady state differentiates it from the thermodynamic equilibrium state. {Quote}: Steady states can be obtained only in open systems, in which changes by internal transformations, e.g., O2 consumption, are instantaneously compensated for by external fluxes across the system boundary, e.g., O2 supply, thus preventing a change of O2 concentration in the system (Gnaiger 1993). Mitochondrial respiratory states monitored in closed systems satisfy the criteria of pseudo-steady states for limited periods of time, when changes in the system (concentrations of O2, fuel substrates, ADP, Pi, H+) do not exert significant effects on metabolic fluxes (respiration, phosphorylation). Such pseudo-steady states require respiratory media with sufficient buffering capacity and substrates maintained at kinetically-saturating concentrations, and thus depend on the kinetics of the processes under investigation. {end of quote: BEC 2020.1). Whereas fluxes may change at a steady state over time, concentrations are maintained constant. The 'respiratory steady state' (Chance and Williams 1955) is characterized by constant fluxes (O2 flux, H2O2 flux) and measured variables of state (cytochrome redox states, Q redox state, NADH redox state, mitochondrial membrane potential). High-resolution respirometry allows for the measurement of several parameters (e.g. O2 flux, H2O2 flux, mitochondrial membrane potential) at pseudo-steady states, when changes of concentrations in the closed system do not exert any control on fluxes. Combination with the Titration-Injection microPump (TIP2k) allows operation with programmable titration regimes at steady-state ADP concentration (Gnaiger 2001), oxygen concentration (oxystat mode; Gnaiger et al 2000, Harrison et al 2015) or steady-state pH (pH-stat more), yielding an expanded flexibility in experimental design by combining the technical advantages of closed and open systems approaches.
Reference: BEC 2020.1, Gnaiger 2000 Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, Gnaiger 2001 Respir Physiol, Harrison 2015 J Appl Physiol
Communicated by Doerrier C 2020-04-20, last update by Gnaiger E 2020-06-02
Hyphenation: Steady state or steady-state?
- Hyphenate if steady-state concentrations are concerned, but do not hyphenate when measurements are made at steady state. - See https://english.stackexchange.com/questions/29333/hyphenating-steady-state
DatLab oxygen flux: performance and data analysis
- Oxygen fluxes should stabilize — reaching a constant value of the rate — before proceeding with the next titration in the SUIT protocol. The following DatLab traces illustrate examples of stable and unstable respiratory rates:
OXPHOS state
Figure 1. Oxygen flux per volume (right axis, red trace) is not stable in the OXPHOS state (2D). Consequently, OXPHOS capacity is underestimated. The addition of cytochrome c (2c), if stability has not yet been reached in the OXPHOS state, leads to an overestimation of the cytochrome c effect, since the increase in the oxygen flux is not due to the cytochrome c addition, but instead because flux increases further over time (see Figure 2 for more detail). Cryopreserved HEK-293 cells. Experiment 2020-01-22 P1-03.
Figure 2. Illustration of (1) the underestimation of OXPHOS capacity (2D), and (2) the overestimation of the cytochrome c effect. The increase of oxygen flux is indicated by the straight line (from 2D to 2c) is not due to the cytochrome c addition. More time would have been requred to reach a stable flux before step 2c. Cryopreserved HEK-293 cells. Experiment 2020-01-22 P1-03.
Figure 3. Oxygen flux is stable in 2D, therefore a proper result on OXPHOS capacity is obtained. In this case, the addition of cytochrome c (2c) does not lead to an overestimation of the cytochrome c control factor. Cryopreserved HEK-293 cells. Experiment 2020-01-22 P5-03_D003 and D007 tests.
Figure 4. Oxygen flux may need time to stabilize (see 2D). Stabilization time is a property of the mitochondrial sample and varies in different pathophysiological states. Stability of flux can be evaluated with the O2k and DatLab at high-resolution by real-time display of oxygen flux (red line). Oxygen concentration (blue line) may appear to show a sufficiently stable slope, while the actual (negative) slope shown by the red line yields the required sensitivity for evaluation of flux in a respiratory 'steady state'. It is important to wait until a steady state is reached to avoid underestimation of respiratory fluxes. Oxygen concentrations may decline below a lower limit in the closed system, in which case a reoxygenation must be performed by intermittently opening the chamber. An instrumental stabilization time must be taken into account after closing the chamber, to avoid an artefact of overestimation of respiratory flux. Therefore, after a reoxygenation it is equally important to wait until an instrumental steady state is reached for measurement of flux. Cryopreserved HEK-293 cells. Experiment 2018-12-18 P8-02.
After addition of inhibitors
Figure 5. Rotenone (Complex I inhibitor) addition in the presence of NS-linked substrates (PGMS) and uncoupler in ET-state (NSE) allows for measurement of S-pathway capacity in the ET state (SE, 6Rot). In many cases, inhibition of flux by rotenone is very fast as shown by a quick transition to a stable flux in the inhibited respiratory state. HEK-293 cells. Experiment 2018-10-23 P8-02.
Figure 6. Inhibition by rotenone (or other inhibitors, e.g. Antimycin A) may require a long time until a new steady respiratory state is reached. This is observed particulary in permeabilized muscle fibers, but may apply to other mitochondrial preparations). It is important to wait until a stable flux is reached to avoid overestimation of respiratory fluxes. HEK-293 cells. Experiment 2018-10-23 P8-02.
References
| Bioblast link | Reference | Year |
|---|---|---|
| Chance 1955 J Biol Chem-III | Chance B, Williams GR (1955) Respiratory enzymes in oxidative phosphorylation: III. The steady state. J Biol Chem 217:409-27. | 1955 |
| Donnelly 2023 MitoFit | Donnelly C, Komlódi T, Cecatto C, Cardoso LHD, Compagnion AC, Matera A, Tavernari D, Zanou N, Kayser B, Gnaiger E, Place N (2023) Functional hypoxia reduces mitochondrial calcium uptake. MitoFit Preprints 2023.2. https://doi.org/10.26124/mitofit:2023-0002 — 2024-11-17 published in Redox Biol. | 2023 |
| Gnaiger 1993 Pure Appl Chem | Gnaiger E (1993) Nonequilibrium thermodynamics of energy transformations. Pure Appl Chem 65:1983-2002. http://dx.doi.org/10.1351/pac199365091983 | 1993 |
| Gnaiger 2001 Respir Physiol | Gnaiger E (2001) Bioenergetics at low oxygen: dependence of respiration and phosphorylation on oxygen and adenosine diphosphate supply. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0034-5687(01)00307-3 | 2001 |
| BEC 2020.1 doi10.26124bec2020-0001.v1 | Gnaiger E et al ― MitoEAGLE Task Group (2020) Mitochondrial physiology. Bioenerg Commun 2020.1. https://doi.org/10.26124/bec:2020-0001.v1 | 2020 |
| Gnaiger 2000 Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A | Gnaiger E, Méndez G, Hand SC (2000) High phosphorylation efficiency and depression of uncoupled respiration in mitochondria under hypoxia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97:11080-5. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.97.20.11080 | 2000 |
| Harrison 2015 J Appl Physiol | Harrison DK, Fasching M, Fontana-Ayoub M, Gnaiger E (2015) Cytochrome redox states and respiratory control in mouse and beef heart mitochondria at steady-state levels of hypoxia. J Appl Physiol 119:1210-8. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.00146.2015 | 2015 |
- Bioblast links: System - >>>>>>> - Click on [Expand] or [Collapse] - >>>>>>>
MitoPedia concepts: "MitoFit Quality Control System" is not in the list (MiP concept, Respiratory state, Respiratory control ratio, SUIT concept, SUIT protocol, SUIT A, SUIT B, SUIT C, SUIT state, Recommended, ...) of allowed values for the "MitoPedia concept" property.
MitoFit Quality Control System"MitoFit Quality Control System" is not in the list (Enzyme, Medium, Inhibitor, Substrate and metabolite, Uncoupler, Sample preparation, Permeabilization agent, EAGLE, MitoGlobal Organizations, MitoGlobal Centres, ...) of allowed values for the "MitoPedia topic" property.
MitoPedia methods:
Respirometry,
Fluorometry,
Spectrophotometry
MitoPedia O2k and high-resolution respirometry:
DatLab