Difference between revisions of "Talk:Malate"
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
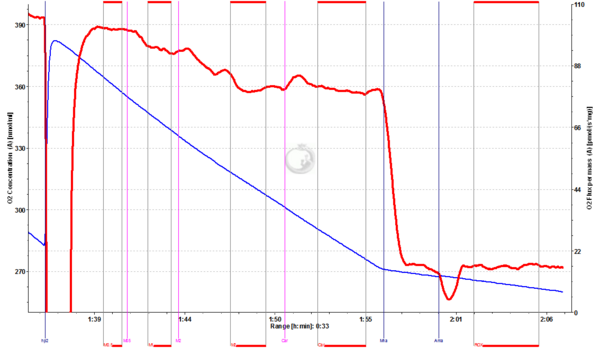
'''Arctic char liver homogenate:''' | |||
[[Image:Char heart homogenate Malate effect.png|600px]] | |||
Fig.2. Arctic Char heart homogenate (1.054 mg/ml, 15°C): [G+M0.5+D5+c+P+S+Reox+U1+U2+U3+U3.5+Rot(not shown)]+M1+M2+Car+Mna+Ama. Heart homogenate respiring at CII-linked ETS was given 1 mM Malate (M1) and 2 mM Malate (M2), which inhibited respiration by 7% and 15%, respectively. Adding Carrier inhibited only 0.9%. | |||
| Line 17: | Line 22: | ||
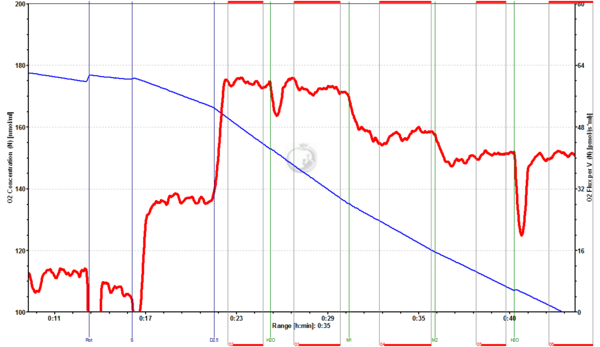
[[Image:Mouse brain homogenate Malate effect.png|600px]] | [[Image:Mouse brain homogenate Malate effect.png|600px]] | ||
Fig. | Fig.3. Mouse brain homogenate (0.9 mg/ml): Rot+S+D2.5+Car1+M1+M2+Car2. Addition of the carrier water (Car1, Car2) had no significant impact on CII-linked OXPHOS (inhibition by 2.2% and -0.2%), whereas the addition of 1 mM Malate (M1) and 2 mM Malate (M2) inhibited respiration by 21% and 11%, respectively. | ||
Revision as of 16:00, 7 February 2014
In the choice of adequate substrates for the evaluation of mitochondrial energetics it is not only the nature but also the quantity that is of crucial importance. Accordingly, we recently tested the concentration of Malate when added together with Pyruvate and/or Glutamate and observed that while Malate stimulates respiration at 0.5 mM concentration, it becomes inhibitory at the generally used concentration of 2 mM. This has been documented for fish liver and heart homogenates (post IOC80 training course), mouse heart, liver and brain homogenate preparations, dog permeabilized skeletal muscle fibers (IOC84), beef heart mitochondria, and brine shrimp (Artemia franciscana) mitochondria.
Some representative examples are displayed below.
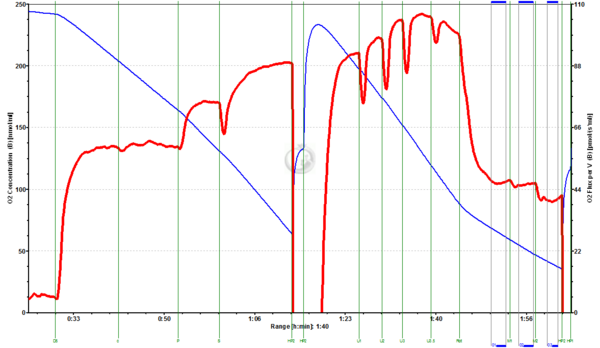
Arctic char liver homogenate:
Fig.1. Arctic Char liver homogenate (3.989 mg/ml, 15°C): GM0.5+D5+c+P+S+Reox+U1+U2+U3+U3.5+Rot+M1+M2. Liver homogenate respiring at CII-linked ETS were given 1 mM Malate (M1) and 2 mM Malate (M2), which inhibited respiration by 1.1% and 13%, respectively.
Arctic char liver homogenate:
Fig.2. Arctic Char heart homogenate (1.054 mg/ml, 15°C): [G+M0.5+D5+c+P+S+Reox+U1+U2+U3+U3.5+Rot(not shown)]+M1+M2+Car+Mna+Ama. Heart homogenate respiring at CII-linked ETS was given 1 mM Malate (M1) and 2 mM Malate (M2), which inhibited respiration by 7% and 15%, respectively. Adding Carrier inhibited only 0.9%.
Mouse brain homogenate:
Fig.3. Mouse brain homogenate (0.9 mg/ml): Rot+S+D2.5+Car1+M1+M2+Car2. Addition of the carrier water (Car1, Car2) had no significant impact on CII-linked OXPHOS (inhibition by 2.2% and -0.2%), whereas the addition of 1 mM Malate (M1) and 2 mM Malate (M2) inhibited respiration by 21% and 11%, respectively.