|
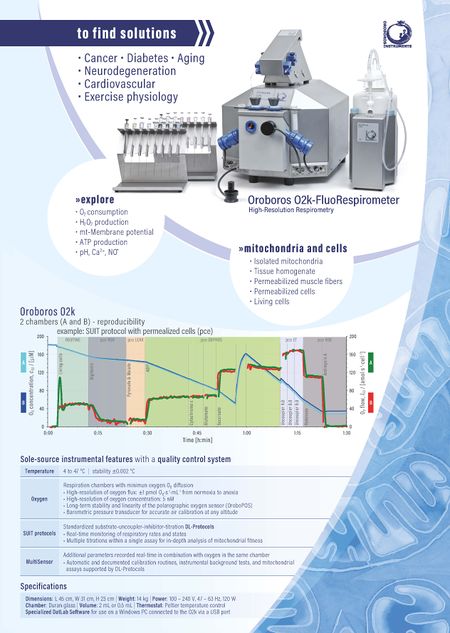
Oroboros specifications |
Description
Oroboros versus multiwell respirometer: The Oroboros Bioenergetics Platform for high-resolution respirometry, the Oroboros O2k and Oroboros NextGen-O2k meet the powerful quality criteria securing high output and pioneering state-of-the-art precision OXPHOS analysis of substrate control and coupling control of mitochondrial function. The limit of detection of O2 flux is as low as 0.5 pmol·s-1·mL-1. Signal noise at zero oxygen concentration is <0.05 μM O2. Oxygen backdiffusion at zero oxygen is <3 pmol·s-1·mL-1, and oxygen consumption at air saturation and standard barometric pressure (100 kPa) was 2.7 ± 0.9 SD in 114 test runs at 37 °C. These highly standardized instrumental background fluxes are a linear function of oxygen concentration, which is used for routine background correction of oxygen flux. Typical exponential time constants of the oxygen sensors are <4 s, used for dynamic corrections in kinetic studies.
If you’re using a biased instrument, it doesn’t matter how many measurements you take – you’re aiming at the wrong target (Silver 2012 Penguin Press). High throughput stands for multiwell systems - expensive, with limited scope and high running costs. In respirometry, high throughput is not equivalent to high output. High output is the concept of the two-chamber Oroboros O2k and NextGen-O2k.
Reference: MiPNet18.10 Oroboros sole source, Flyer with specification summary
Oroboros: technical specifications
- The Oroboros with DatLab software is world-wide the only instrument (sole source) which allows routine measurements to be made with specifications summarized under the term high-resolution respirometry (HRR). The sole-source Oroboros specifications distinguish high-resolution respirometry from any conventional oxygraph system and from less quantitative approaches.
General specifications
- Dimensions - Oroboros Main Unit: L 45 cm, W 31 cm, H 25 cm; 13.45 kg without packing box or Peli Case.
- Two experimental chambers: Duran glass, chemically inert, and minimum oxygen diffusion:
- - classic-volume 2 mL (cV; 1.5 to 3.0 mL; 16 mm inner diameter)
- - small-volume 0.5 mL (sV; 0.5 to 1.0 mL; 12 mm inner diameter)
- - PEEK stoppers with Viton O-rings
- Electromagnetic stirrer bars PVDF-coated AlNiCo, variable rotation speed (26 to 900 rpm)
- - cV: 15.0 x 6.5 mm, optimal rotation speed 750 rpm (12.5 Hz)
- - sV: 11.5 x 6.2 mm, optimal rotation speed 550 rpm (9.16 Hz)
- Polarographic oxygen sensors sealed with butyl rubber seal tips
- Built-in electronically regulated Peltier thermostat:
- - Temperature range:
At room temperature 4 °C to 47 °C At lower ambient temperature 2 °C to 47 °C
- - Temperature stability:
Temperature stability ±0.002 °C over 90 min
- - Temperature stabilization time:
15 min 20 °C to 30 °C 20 min 30 °C to 20 °C
- Data output through USB port:
- - Two oxygen signals
- - Pressure transducer, for absolute barometric pressure signal, resolution 0.1 kPa
- - Thermostat temperature signal, resolution 0.001 °C
- - Oroboros MultiSensor:
- O2k Series J and NextGen-O2k Series XB
- two additional amperometric signals (O2k-fluorescence; PhotoBiology)
- two additional potentiometric signals (Ion-selective electrodes: for TPP+, Ca2+, or pH)
- NextGen-O2k Series XB
- two additional amperometric signals for Q redox state
- two additional amperometric signals (NO)
- - Oroboros MultiSensor:
- DatLab software:
- - Simultaneous display of O2 concentration and O2 flux (negative slope or time derivative), together with any selected MultiSensor channels (raw or calibrated signals and corresponding time derivatives)
- - Barometric pressure for O2 calibration; temperature stability control
- - Automatic calibrations: O2 and MultiSensor channels
- - DL-Protocols: real-time guide through instrumental quality control tests and advanced diagnostic substrate-uncoupler-inhibitor titration (SUIT) protocols within a single assay for exploring mitochondrial function
- internal PC and attached screen
Specifications for high-resolution respirometry
- Oxygen signal:
- - Noise at zero O2: <±0.02 µM (SD, 100 data points recorded at 0.2 s intervals at 37 °C) without smoothing (±0.005 µM typical)
- - Noise at zero O2: <±0.002 kPa (SD, 100 data points recorded at 0.2 s intervals) without smoothing (±0.0005 kPa typical)
- - Noise at air saturation: <±0.1 µM O2 (SD, 100 data points recorded 0.2 s intervals at 37 °C) without smoothing, at 180 µM O2 (±0.05 µM typical)
- - Noise at air saturation: <±0.01 kPa (SD, 100 data points recorded 0.2 s intervals) without smoothing, at partial oxygen pressure of 20 kPa (±0.005 kPa typical)
- - O2 range of linearity: 0 to 1000 µM
- - Time constant: <4 s at 37 °C (<3 s typical)
- Oxygen flux JO2,V [pmol·s-1·mL-1]:
- - Limit of detection: 0.5 at steady-state over 5 min
- - Sensitivity (normoxic): <1 at steady-state over 5 min at 20-40 °C
- - Sensitivity (hyperoxic): <3 at steady-state over 5 min at 20-40 °C
- - Noise: <0.2 after standard smoothing (120 s)
- - O2 range: flux measured up to 500 µM O2 (permeabilized fibres), and <0.1 µM based on DatLab analysis of oxygen kinetics (mitochondria and cells)
- Instrumental background for linear correction over the entire oxygen range:
- - O2 backdiffusion [pmol·s-1·mL-1] at 0 µM: <3 at 20-40 °C (2.5 typical)
- - O2 backdiffusion [pmol·s-1·mL-1] at 0 kPa: <3 at 20-40 °C (2.5 typical)
- - O2 consumption [pmol·s-1·mL-1] at 200 µM: <4 at 37 °C (3 typical); <3 at 25 °C (2 typical)
- - O2 consumption [pmol·s-1·mL-1] at 20 kPa: <4 at 37 °C (3 typical); <3 at 25 °C (2 typical)
Selected references
Comparison of respirometric methods - Discussion
- Gnaiger E (2024) Oroboros instrument specifications for high-resolution respirometry and precision OXPHOS analysis. Mitochondr Physiol Network 18.10(11):1-14.
- Baglivo E, Cardoso LHD, Cecatto C, Gnaiger E (2024) Stability of mitochondrial respiration medium used in high-resolution respirometry with living and permeabilized cells. Bioenerg Commun 2024.8. https://doi.org/10.26124/bec.2024-0008
- Donnelly C, Komlódi T, Cecatto C, Cardoso LHD, Compagnion A-C, Matera A, Tavernari D, Campiche O, Paolicelli RC, Zanou N, Kayser B, Gnaiger E, Place N (2024) Functional hypoxia reduces mitochondrial calcium uptake. Redox Biol 71:103037. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2024.103037
- Doerrier C, Gama-Perez P, Pesta D, Distefano G, Soendergaard SD, Maise Chroeis K, Gonzalez-Franquesa A, Goodpaster BH, Prats C, Sales-Pardo M, Guimera R, Coen PM, Gnaiger E, Larsen S, Garcia-Roves PM (2024) Harmonization of experimental procedures to assess mitochondrial respiration in human permeabilized skeletal muscle fibers. Free Radic Biol Med 223:384-97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2024.07.039
- Gnaiger E (2024) Complex II ambiguities ― FADH2 in the electron transfer system. J Biol Chem 300:105470. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2023.105470
- Pfleger A, Arc E, Grings M, Gnaiger E, Roach T (2024) Flavodiiron proteins prevent the Mehler reaction in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Biochim Biophys Acta Bioenerg 1865:149497. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbabio.2024.149497
- Scandalis L, Kitzman DW, Nicklas BJ, Lyles M, Brubaker P, Nelson MB, Gordon M, Stone J, Bergstrom J, Neufer PD, Gnaiger E, Molina AJA (2023) Skeletal muscle mitochondrial respiration and exercise intolerance in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. JAMA Cardiol 8:575–84. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamacardio.2023.0957
- Zdrazilova L, Hansikova H, Gnaiger E (2022) Comparable respiratory activity in attached and suspended human fibroblasts. PLoS ONE 17:e0264496. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0264496
- Donnelly C, Schmitt S, Cecatto C, Cardoso LHD, Komlódi T, Place N, Kayser B, Gnaiger E (2022) The ABC of hypoxia – what is the norm. Bioenerg Commun 2022.12.v2. https://doi.org/10.26124/bec:2022-0012.v2
- Gnaiger E (2021) Beyond counting papers – a mission and vision for scientific publication. Bioenerg Commun 2021.5. https://doi.org/10.26124/bec:2021-0005
- Cardoso LHD, Doerrier C, Gnaiger E (2021) Magnesium Green for fluorometric measurement of ATP production does not interfere with mitochondrial respiration. Bioenerg Commun 2021.1. https://doi.org/10.26124/bec:2021-0001
- Komlódi T, Cardoso LHD, Doerrier C, Moore AL, Rich PR, Gnaiger E (2021) Coupling and pathway control of coenzyme Q redox state and respiration in isolated mitochondria. Bioenerg Commun 2021.3. https://doi.org/10.26124/bec:2021-0003
- Komlódi T, Sobotka O, Gnaiger E (2021) Facts and artefacts on the oxygen dependence of hydrogen peroxide production using Amplex UltraRed. Bioenerg Commun 2021.4. https://doi.org/10.26124/bec:2021-0004
- Gnaiger E (2021) Bioenergetic cluster analysis – mitochondrial respiratory control in human fibroblasts. MitoFit Preprints 2021.08. https://doi.org/10.26124/mitofit:2021-0008
- Gnaiger E (2021) The elementary unit — canonical reviewer's comments on: Bureau International des Poids et Mesures (2019) The International System of Units (SI) 9th ed. MitoFit Preprints 2020.04.v2. https://doi.org/10.26124/mitofit:200004.v2
- Gnaiger E (2020) Mitochondrial pathways and respiratory control. An introduction to OXPHOS analysis. 5th ed. Bioenerg Commun 2020.2. https://doi.org/10.26124/bec:2020-0002
- Gnaiger E et al ― MitoEAGLE Task Group (2020) Mitochondrial physiology. Bioenerg Commun 2020.1. https://doi.org/10.26124/bec:2020-0001.v1
- Schöpf B, Weissensteiner H, Schäfer G, Fazzini F, Charoentong P, Naschberger A, Rupp B, Fendt L, Bukur V, Giese I, Sorn P, Sant’Anna-Silva AC, Iglesias-Gonzalez J, Sahin U, Kronenberg F, Gnaiger E, Klocker H (2020) OXPHOS remodeling in high-grade prostate cancer involves mtDNA mutations and increased succinate oxidation. Nat Commun 11:1487. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-15237-5
- Chicco AJ, Le CH, Gnaiger E, Dreyer HC, Muyskens JB, D'Alessandro A, Nemkov T, Hocker AD, Prenni JE, Wolfe LM, Sindt NM, Lovering AT, Subudhi AW, Roach RC (2018) Adaptive remodeling of skeletal muscle energy metabolism in high-altitude hypoxia: Lessons from AltitudeOmics. J Biol Chem 293:6659-71.
- Doerrier C, Garcia-Souza LF, Krumschnabel G, Wohlfarter Y, Mészáros AT, Gnaiger E (2018) High-Resolution FluoRespirometry and OXPHOS protocols for human cells, permeabilized fibers from small biopsies of muscle, and isolated mitochondria. Methods Mol Biol 1782:31-70. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-7831-1_3
- Horscroft JA, Kotwica AO, Laner V, West JA, Hennis PJ, Levett DZH, Howard DJ, Fernandez BO, Burgess SL, Ament Z, Gilbert-Kawai ET, Vercueil A, Landis BD, Mitchell K, Mythen MG, Branco C, Johnson RS, Feelisch M, Montgomery HE, Griffin JL, Grocott MPW, Gnaiger E, Martin DS, Murray AJ (2017) Metabolic basis to Sherpa altitude adaptation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 114:6382–7. - »Bioblast link«
- Lemieux H, Blier PU, Gnaiger E (2017) Remodeling pathway control of mitochondrial respiratory capacity by temperature in mouse heart: electron flow through the Q-junction in permeabilized fibers. Sci Rep 7:2840. - »Bioblast link«
- Miller B, Hamilton K, Boushel R, Williamson K, Laner V, Gnaiger E, Davis M (2017) Mitochondrial respiration in highly aerobic canines in the non-raced state and after a 1600-km sled dog race. PLOS ONE 12:e0174874. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0174874
- Gnaiger E, Boushel R, Søndergaard H, Munch-Andersen T, Damsgaard R, Hagen C, Díez-Sánchez C, Ara I, Wright-Paradis C, Schrauwen P, Hesselink M, Calbet JAL, Christiansen M, Helge JW, Saltin B (2015) Mitochondrial coupling and capacity of oxidative phosphorylation in skeletal muscle of Inuit and caucasians in the arctic winter. Scand J Med Sci Sports 25 (Suppl 4):126–34. - »Bioblast link«
- Harrison DK, Fasching M, Fontana-Ayoub M, Gnaiger E (2015) Cytochrome redox states and respiratory control in mouse and beef heart mitochondria at steady-state levels of hypoxia. J Appl Physiol 119:1210-8. - »Bioblast link«
- Makrecka-Kuka M, Krumschnabel G, Gnaiger E (2015) High-resolution respirometry for simultaneous measurement of oxygen and hydrogen peroxide fluxes in permeabilized cells, tissue homogenate and isolated mitochondria. Biomolecules 5:1319-38. - »Bioblast link«
- Votion DM, Gnaiger E, Lemieux H, Mouithys-Mickalad A, Serteyn D (2012) Physical fitness and mitochondrial respiratory capacity in horse skeletal muscle. PLoS One 7: e34890. |»Bioblast link«
- Lemieux H, Semsroth S, Antretter H, Höfer D, Gnaiger E (2011) Mitochondrial respiratory control and early defects of oxidative phosphorylation in the failing human heart. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 43:1729–38. - »Bioblast link«
- Pesta D, Hoppel F, Macek C, Messner H, Faulhaber M, Kobel C, Parson W, Burtscher M, Schocke M, Gnaiger E (2011) Similar qualitative and quantitative changes of mitochondrial respiration following strength and endurance training in normoxia and hypoxia in sedentary humans. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 301:R1078–87. - »Bioblast link«
- Scandurra FM, Gnaiger E (2010) Cell respiration under hypoxia: facts and artefacts in mitochondrial oxygen kinetics. Adv Exp Med Biol 662:7-25. - »Bioblast link«
- Aguirre E, Rodríguez-Juárez F, Bellelli A, Gnaiger E, Cadenas S (2010) Kinetic model of the inhibition of respiration by endogenous nitric oxide in intact cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 1797:557-65. - |»Bioblast link«
- Aragonés J, Schneider M, Van Geyte K, Fraisl P, Dresselaers T, Mazzone M, Dirkx R, Zacchigna S, Lemieux H, Jeoung NH, Lambrechts D, Bishop T, Lafuste P, Diez-Juan A, K Harten S, Van Noten P, De Bock K, Willam C, Tjwa M, Grosfeld A, Navet R, Moons L, Vandendriessche T, Deroose C, Wijeyekoon B, Nuyts J, Jordan B, Silasi-Mansat R, Lupu F, Dewerchin M, Pugh C, Salmon P, Mortelmans L, Gallez B, Gorus F, Buyse J, Sluse F, Harris RA, Gnaiger E, Hespel P, Van Hecke P, Schuit F, Van Veldhoven P, Ratcliffe P, Baes M, Maxwell P, Carmeliet P (2008) Deficiency or inhibition of oxygen sensor Phd1 induces hypoxia tolerance by reprogramming basal metabolism. Nat Genet 40:170-80. - »Bioblast link«
- Gnaiger E (2008) Polarographic oxygen sensors, the oxygraph and high-resolution respirometry to assess mitochondrial function. In: Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Drug-Induced Toxicity (Dykens JA, Will Y, eds) John Wiley:327-52. - »Bioblast link«
- Hütter E, Renner K, Pfister G, Stöckl P, Jansen-Dürr P, Gnaiger E (2004) Senescence-associated changes in respiration and oxidative phosphorylation in primary human fibroblasts. Biochem J 380:919-28. - »Bioblast link«
- Kuznetsov AV, Schneeberger S, Seiler R, Brandacher G, Mark W, Steurer W, Saks V, Usson Y, Margreiter R, Gnaiger E (2004) Mitochondrial defects and heterogeneous cytochrome c release after cardiac cold ischemia and reperfusion. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 286:H1633–41. - »Bioblast link«
- Gnaiger E (2001) Bioenergetics at low oxygen: dependence of respiration and phosphorylation on oxygen and adenosine diphosphate supply. Respir Physiol 128:277-97. - »Bioblast link«
- Gnaiger E, Méndez G, Hand SC (2000) High phosphorylation efficiency and depression of uncoupled respiration in mitochondria under hypoxia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97:11080-5. »Open Access«
- Steinlechner-Maran R, Eberl T, Kunc M, Margreiter R, Gnaiger E (1996) Oxygen dependence of respiration in coupled and uncoupled endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 271:C2053-61. - »Bioblast link«
- Gnaiger E, Steinlechner-Maran R, Méndez G, Eberl T, Margreiter R (1995) Control of mitochondrial and cellular respiration by oxygen. J Bioenerg Biomembr 27:583-96. - »Bioblast link«
MitoPedia: Oroboros hardware, Oroboros Open Support, O2k-Respirometry, O2k-FluoRespirometry