Difference between revisions of "Coupling/pathway control diagram"
| (7 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
|abbr=CPCD | |abbr=CPCD | ||
|description=[[File:SUIT-nomenclature.jpg|300px|right|SUIT protocols]] | |description=[[File:SUIT-nomenclature.jpg|300px|right|SUIT protocols]] | ||
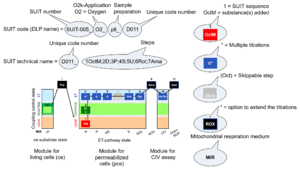
'''Coupling/pathway control diagrams''' illustrate the respiratory '''states''' obtained step-by-step in substrate-uncoupler-inhibitor titrations in a [[SUIT protocol]]. Each step (to the next state) is defined by an initial state and a [[metabolic control variable]], ''X''. The respiratory states are shown by boxes. ''X'' is usually the titrated substance in a SUIT protocol. If ''X'' ([[ADP]], [[uncoupler]]s, or inhibitors of the [[phosphorylation system]], e.g. oligomycin) exerts '''coupling control''', then a transition is induced between two [[coupling control state]]s. If ''X'' (fuel substrates, e.g. pyruvate and succinate, or [[ | '''Coupling/pathway control diagrams''' illustrate the respiratory '''states''' obtained step-by-step in substrate-uncoupler-inhibitor titrations in a [[SUIT protocol]]. Each step (to the next state) is defined by an initial state and a [[metabolic control variable]], ''X''. The respiratory states are shown by boxes. ''X'' is usually the titrated substance in a SUIT protocol. If ''X'' ([[ADP]], [[uncoupler]]s, or inhibitors of the [[phosphorylation system]], e.g. oligomycin) exerts '''coupling control''', then a transition is induced between two [[coupling-control state]]s. If ''X'' (fuel substrates, e.g. pyruvate and succinate, or [[Electron transfer pathway]] inhibitors, e.g. rotenone) exerts '''pathway control''', then a transition is induced between two [[Electron-transfer-pathway state]]s. The type of metabolic control (''X'') is shown by arrows linking two respiratory states, with vertical arrows indicating coupling control, and horizontal arrows indicating pathway control. [[Marks - DatLab |Marks]] define the section of an experimental trace in a given [[respiratory state]] (steady state). [[Events - DatLab |Events]] define the titration of ''X'' inducing a transition in the SUIT protocol. The specific sequence of coupling control and pathway control steps defines the [[SUIT protocol pattern]]. The coupling/pathway control diagrams define the [[categories of SUIT protocols]] (see Figure). | ||
|info=[[Gnaiger | |info=[[Gnaiger 2020 BEC MitoPathways]] | ||
}} | }} | ||
Communicated by [[Gnaiger Erich]] 2016-06-07, edited 2016-10-31. | Communicated by [[Gnaiger Erich]] 2016-06-07, edited 2016-10-31. | ||
| Line 14: | Line 11: | ||
::::» [[Categories of SUIT protocols]] | ::::» [[Categories of SUIT protocols]] | ||
{{MitoPedia concepts | |||
|mitopedia concept=MiP concept, SUIT concept | |||
}} | |||
Latest revision as of 20:03, 1 January 2021
- high-resolution terminology - matching measurements at high-resolution
Coupling/pathway control diagram
Description
Coupling/pathway control diagrams illustrate the respiratory states obtained step-by-step in substrate-uncoupler-inhibitor titrations in a SUIT protocol. Each step (to the next state) is defined by an initial state and a metabolic control variable, X. The respiratory states are shown by boxes. X is usually the titrated substance in a SUIT protocol. If X (ADP, uncouplers, or inhibitors of the phosphorylation system, e.g. oligomycin) exerts coupling control, then a transition is induced between two coupling-control states. If X (fuel substrates, e.g. pyruvate and succinate, or Electron transfer pathway inhibitors, e.g. rotenone) exerts pathway control, then a transition is induced between two Electron-transfer-pathway states. The type of metabolic control (X) is shown by arrows linking two respiratory states, with vertical arrows indicating coupling control, and horizontal arrows indicating pathway control. Marks define the section of an experimental trace in a given respiratory state (steady state). Events define the titration of X inducing a transition in the SUIT protocol. The specific sequence of coupling control and pathway control steps defines the SUIT protocol pattern. The coupling/pathway control diagrams define the categories of SUIT protocols (see Figure).
Abbreviation: CPCD
Reference: Gnaiger 2020 BEC MitoPathways
Communicated by Gnaiger Erich 2016-06-07, edited 2016-10-31.
See also
MitoPedia concepts:
MiP concept,
SUIT concept