Talk:Numeral
From Bioblast
The energy of numerals
What is written here for numbers should consider numerals.
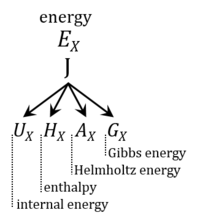
- Energy is a fundamental quantity of physics with the SI unit joule [J]. The first law of thermodynamics makes the familiar statement that energy is constant, in the sense that it cannot be produced or destroyed, as long as one stays away from the domain of relativity theory. The second law of thermodynamics, however, claims that a particular form of energy (better termed exergy) can be and must be destroyed as long as the final state of equilibrium is not reached. Thus the term 'energy' is ambiguous, since there are different forms of energy (Figure 11).
- It is tempting to consider numbers with different energies in analogy to the different forms of energy. This may resolve the difficulty to distinguish a number from its numerical value. Counting nuts or stones, and the numerals on regular dice as symbols for the numbers 1 to 6 provide a help to get a feeling for the energy of numbers. Numbers with different energies are in different states of realization. To avoid confusion between a pure number N and a count NX, consider the definition of a count as the product of a number N and an elementary entity UX.
Physical numbers
- The potential energy of a stone mounted at a paricular height is the energy that can be retrieved potentially when coupling its fall to the ground with an energy-transforming process, without which the energy is dissipated as heat. Consider the potential number as any of the six numbers on a die, which may show on the top after rolling the die. The potential number is the single number of the set of possible numbers, which will be realized after rolling the die. The set of possible numbers on a physical device limits the range of potential numbers that can possibly be realized. This kind of potential number belongs to the order of physical numbers.
- Another physical number is the static number, which is the numerical value on top of a die realized after having rolled the die, or the numerical value of a count of stones in a box. A static number has a defined numerical value, whereas a potential number has only the probability that a particular numerical value will be realized. But if the die is not rolled, or the value of N is not known when the stones in the black box are not counted, the count NX has no defined value.
- A dynamic number or dynamic numerical value may be seen as the number added to the side of a die when making the die. This is the highly dynamic process of creating a new number. The number of numbers (this is a count) in the universe is not a constant. Type a digital number into your computer — push a button and you are the creator of a new number. You may cut a number into stone or write a number on paper — you are a number maker. If you burn a regular wooden die, there will be a loss of six numbers in the world. Less dramatically, a dynamic number is related to events. When a stone is moved into or out of a box, then this is an event that may help to count the change of the number of stones in the box. From the perspective of the box, throwing a stone into the box is a count with a positive number, picking a stone out of the box is a count with a negative number. Any number of, is not a number, but is a count; the count has a numerical value which is a number of something physically real.
Virtual numbers
- Virtual numbers are abstract and used by mathematicians. More specifically, an abstract number is a virtual number of a virtual die realized without rolling the die, or a virtual number of abstract stones in an abstract box. All types of physical numbers can be imagined or realized as virtual numbers. Mathematical numbers, however, are virtual numbers realized without any abstraction from a physical thing as a theoretical reference. Since the universe contains a limited number of particles, an infinite number can only be a mathematical number used by mathematicians, and not an abstract number with a physical reference of the imagination in the real world.