Difference between revisions of "Talk:O2k-pH ISE-Module"
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
"At high fructose concentrations, respiration is inhibited while glycolytic end products accumulate, a phenomenon known as the Crabtree effect. It is commonly believed that this effect is restricted to microbial and tumour cells with uniquely high glycolytic capacities (Sussman et al, 1980). However, inhibition of respiration and increase of lactate production are observed under aerobic conditions in beating rat heart cell cultures (Frelin et al, 1974) and in isolated rat lung cells (Ayuso-Parrilla et al, 1978). Thus, the same general mechanisms responsible for the integration of respiration and glycolysis in tumour cells (Sussman et al, 1980) appear to be operating to some extent in several isolated mammalian cells." [[Gnaiger 1990 Biochim Biophys Acta]] | "At high fructose concentrations, respiration is inhibited while glycolytic end products accumulate, a phenomenon known as the Crabtree effect. It is commonly believed that this effect is restricted to microbial and tumour cells with uniquely high glycolytic capacities (Sussman et al, 1980). However, inhibition of respiration and increase of lactate production are observed under aerobic conditions in beating rat heart cell cultures (Frelin et al, 1974) and in isolated rat lung cells (Ayuso-Parrilla et al, 1978). Thus, the same general mechanisms responsible for the integration of respiration and glycolysis in tumour cells (Sussman et al, 1980) appear to be operating to some extent in several isolated mammalian cells." [[Gnaiger 1990 Biochim Biophys Acta]] | ||
== Demo Experiment with simulated proton flow == | == Demo Experiment with simulated proton flow == | ||
Revision as of 10:34, 8 September 2018
Previous Product ID 33000-01
MultiSensor-O2k: Oxygen and pH - Warburg versus Crabtree Effect
Q: For quantification of aerobic glycolysis in intact cells, the measurement of proton production can be used as an indirect but continuous record of lactate production and corresponding acidification of the medium, while simultaneously monitoring oxygen concentration and oxygen consumption (MultiSensor-O2k). Is this related to the Warburg or Crabtree effect?
A: Under various metabolic conditions, lactic acid production is the dominant mechanism causing acidification, hence the pH measurement is a good indirect indicator of aerobic glycolysis. An early paper summarizing the literature in this field states:
"At high fructose concentrations, respiration is inhibited while glycolytic end products accumulate, a phenomenon known as the Crabtree effect. It is commonly believed that this effect is restricted to microbial and tumour cells with uniquely high glycolytic capacities (Sussman et al, 1980). However, inhibition of respiration and increase of lactate production are observed under aerobic conditions in beating rat heart cell cultures (Frelin et al, 1974) and in isolated rat lung cells (Ayuso-Parrilla et al, 1978). Thus, the same general mechanisms responsible for the integration of respiration and glycolysis in tumour cells (Sussman et al, 1980) appear to be operating to some extent in several isolated mammalian cells." Gnaiger 1990 Biochim Biophys Acta
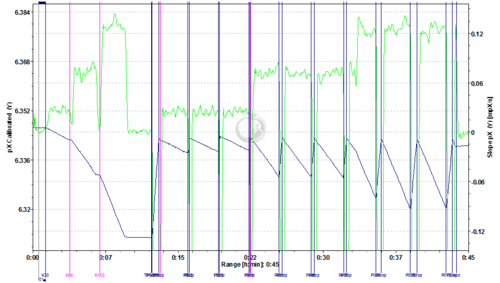
Demo Experiment with simulated proton flow
- Medium: imidazole buffered medium, see above
- Calibration steps (for calculating buffering capacity): 30, 90, 150 HCl pmol/ (ml s): TIP 1 mmol/l HCl, pump speed 0.06, 0.18, 0.3 µl/s
- Simulated proton flow 30,90,150 pmol HCl/(ml s) in pH stat mode: The pH value was held inside narrow limits by using the TIP in pH stat mode (100 mM KOH, Tip set up similar to the one included in DLTemplates_pH.dlt available from http://www.oroboros.at/index.php?id=ph-oxygen. The proton flow was simulated using a second TIP
Popular Bioblast page
- O2k-pH ISE-Module has been accessed more than
- 20,000 times (2017-01-15)
- 15,000 times (2015-01-18)
- 10,000 times (2014-11-13)
- 5,000 times (2013-11-06)
- O2k-pH ISE-Module has been accessed more than