Difference between revisions of "Metabolic control variable"
| (14 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{MitoPedia | {{MitoPedia | ||
|abbr=''X'' | |abbr=''X'' | ||
|description=A '''metabolic control variable''' | |description=A '''metabolic control variable''' ''X'' causes the transition between a [[background state]] Y (background rate ''Y<sub>X</sub>'') and a [[reference state]] Z (reference rate ''Z<sub>X</sub>''). ''X'' may be a stimulator or activator of flux, inducing the step change from background to reference steady state (Y to Z). Alternatively, ''X'' may be an inhibitor of flux, absent in the reference state but present in the background state (step change from Z to Y). | ||
|info=[[ | |info=[[Flux control efficiency]] | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{MitoPedia | Communicated by [[Gnaiger E]] (2013-08-03) last update 2020-11-10. | ||
|mitopedia | |||
== Keywords == | |||
{{Template:Keywords: Coupling control}} | |||
{{MitoPedia concepts | |||
|mitopedia concept=MiP concept, Respiratory control ratio, SUIT concept, Ergodynamics | |||
}} | }} | ||
{{MitoPedia topics | {{MitoPedia topics | ||
|mitopedia topic= | |mitopedia topic=Inhibitor, Substrate and metabolite, Uncoupler | ||
}} | }} | ||
Latest revision as of 18:19, 10 November 2020
Description
A metabolic control variable X causes the transition between a background state Y (background rate YX) and a reference state Z (reference rate ZX). X may be a stimulator or activator of flux, inducing the step change from background to reference steady state (Y to Z). Alternatively, X may be an inhibitor of flux, absent in the reference state but present in the background state (step change from Z to Y).
Abbreviation: X
Reference: Flux control efficiency
Communicated by Gnaiger E (2013-08-03) last update 2020-11-10.
Keywords
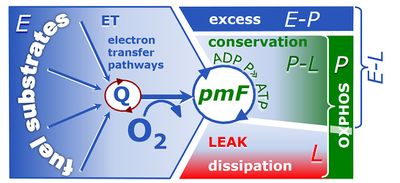
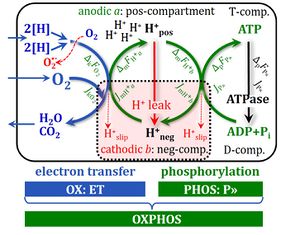
4-compartmental OXPHOS model. (1) ET capacity E of the noncoupled electron transfer system ETS. OXPHOS capacity P is partitioned into (2) the dissipative LEAK component L, and (3) ADP-stimulated P-L net OXPHOS capacity. (4) If P-L is kinetically limited by a low capacity of the phosphorylation system to utilize the protonmotive force pmF, then the apparent E-P excess capacity is available to drive coupled processes other than phosphorylation P» (ADP to ATP) without competing with P».
- Bioblast links: Coupling control - >>>>>>> - Click on [Expand] or [Collapse] - >>>>>>>
1. Mitochondrial and cellular respiratory rates in coupling-control states
| Respiratory rate | Defining relations | Icon | |
|---|---|---|---|
| OXPHOS capacity | P = P´-Rox | mt-preparations | |
| ROUTINE respiration | R = R´-Rox | living cells | |
| ET capacity | E = E´-Rox | » Level flow | |
| » Noncoupled respiration - Uncoupler | |||
| LEAK respiration | L = L´-Rox | » Static head | |
| » LEAK state with ATP | |||
| » LEAK state with oligomycin | |||
| » LEAK state without adenylates | |||
| Residual oxygen consumption Rox | L = L´-Rox |
2. Flux control ratios related to coupling in mt-preparations and living cells
| FCR | Definition | Icon | |
|---|---|---|---|
| L/P coupling-control ratio | L/P | » Respiratory acceptor control ratio, RCR = P/L | |
| L/R coupling-control ratio | L/R | ||
| L/E coupling-control ratio | L/E | » Uncoupling-control ratio, UCR = E/L (ambiguous) | |
| P/E control ratio | P/E | ||
| R/E control ratio | R/E | » Uncoupling-control ratio, UCR = E/L | |
| net P/E control ratio | (P-L)/E | ||
| net R/E control ratio | (R-L)/E |
3. Net, excess, and reserve capacities of respiration
| Respiratory net rate | Definition | Icon |
|---|---|---|
| P-L net OXPHOS capacity | P-L | |
| R-L net ROUTINE capacity | R-L | |
| E-L net ET capacity | E-L | |
| E-P excess capacity | E-P | |
| E-R reserve capacity | E-R |
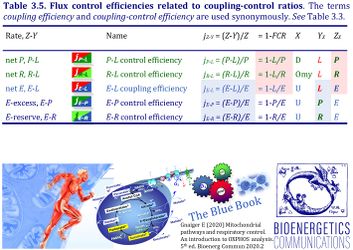
4. Flux control efficiencies related to coupling-control ratios
| Coupling-control efficiency | Definition | Icon | Canonical term | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P-L control efficiency | jP-L | = (P-L)/P | = 1-L/P | P-L OXPHOS-flux control efficiency | |
| R-L control efficiency | jR-L | = (R-L)/R | = 1-L/R | R-L ROUTINE-flux control efficiency | |
| E-L coupling efficiency | jE-L | = (E-L)/E | = 1-L/E | E-L ET-coupling efficiency » Biochemical coupling efficiency | |
| E-P control efficiency | jE-P | = (E-P)/E | = 1-P/E | E-P ET-excess flux control efficiency | |
| E-R control efficiency | jE-R | = (E-R)/E | = 1-R/E | E-R ET-reserve flux control efficiency |
5. General
- » Basal respiration
- » Cell ergometry
- » Dyscoupled respiration
- » Dyscoupling
- » Electron leak
- » Electron-transfer-pathway state
- » Hyphenation
- » Oxidative phosphorylation
- » Oxygen flow
- » Oxygen flux
- » Permeabilized cells
- » Phosphorylation system
- » Proton leak
- » Proton slip
- » Respiratory state
- » Uncoupling
MitoPedia concepts:
MiP concept,
Respiratory control ratio,
SUIT concept,
Ergodynamics
MitoPedia topics:
Inhibitor,
Substrate and metabolite,
Uncoupler